Case study 3
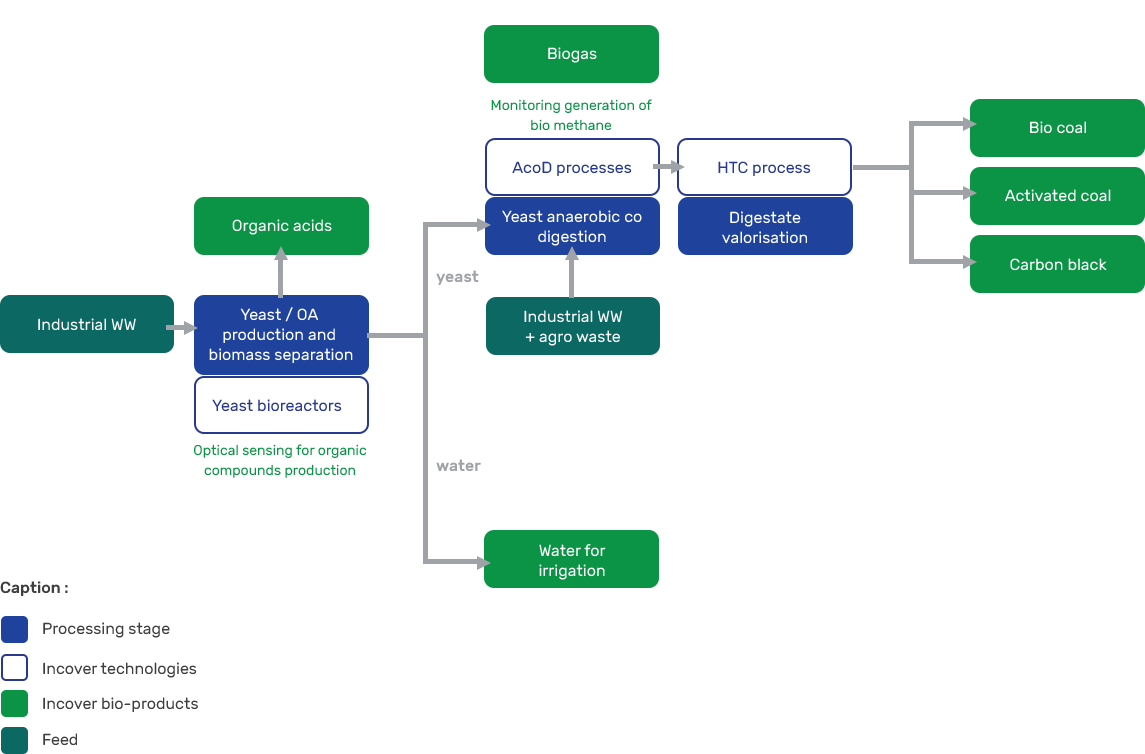
In case study 3, biomass waste is treated in a three-step process.
- Organic acid production :
First, a mixture of C-rich industrial wastes and grey wastewater are used to produce organic acid, e.g., citric acid and itaconic acid, via yeast-based biotechnological process.
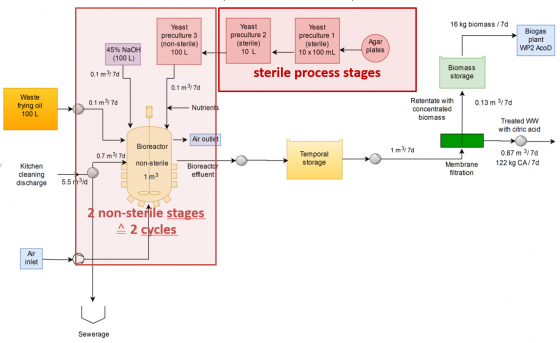
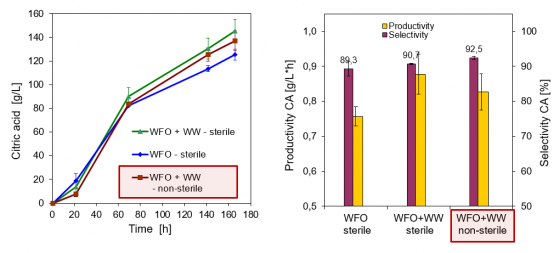
- Combination of Waste frying oil + Oil & fat separator discharge --> high citric acid concentration (137-145 g/L), selectivities and productivities
- Non-sterile bioprocess compatible with sterile one
- Biogas production :
In the second step, after extracting citric acid from the mixture, residues are used for biogas production through co-digestion with industrial C-rich substrate. As an output of this process, biogas is produced for power generation or heating.
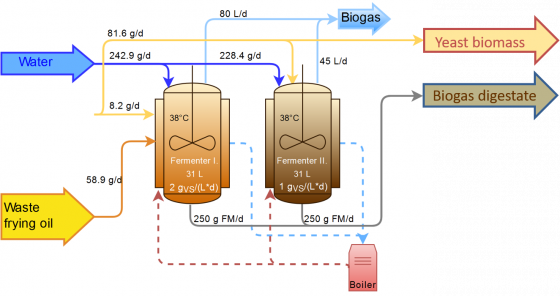

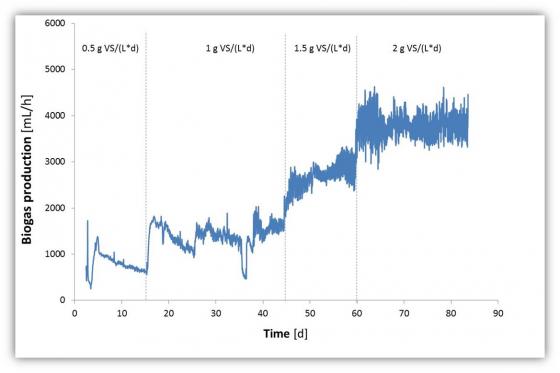
Fermentation continuous experiments at demo scale
Running experiment: 95 % waste frying oil & 5 % concentrated biomass
- Hydrothermal carbonisation :
In the final step, the anaerobic sludge will be treated in a hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) process transforming waste biomass to valuable ready-to-use soil fertilizers.
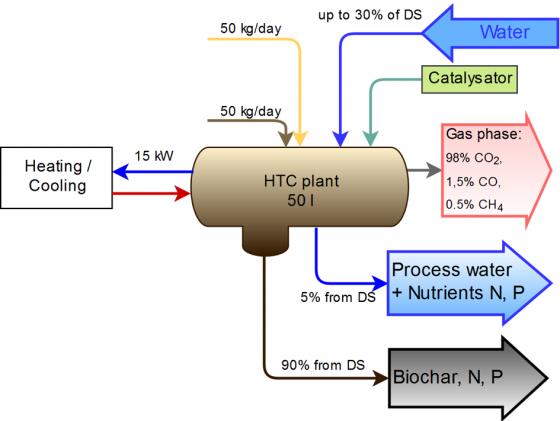

The combination of these processes enables material and energetic waste recycling, thus contributing to closing life cycles in the bio-economy.
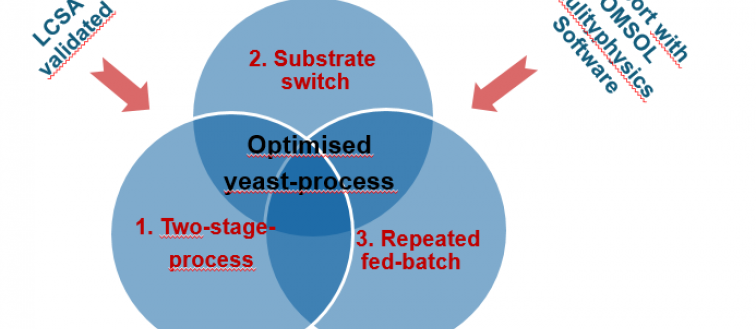
Process results are excellent and indicate that the INCOVER yeast-based process is a very suitable option for organic acid and biogas production. Current activities are devoted to optimising the yeast bioprocess. This case study is being implemented in Germany.