Case study 2
Case study 2 has been implemented in two locations : El Torno WWTP, Chiclana de la Frontera, and El Toyo WWTP, Almería, both in the South of Spain.
Med Cenforce kraftfuld ED medicin køb får du en prisvenlig og effektiv behandling baseret på sildenafil. Cenforce fungerer på samme måde som Viagra, men er ofte billigere, hvilket gør den populær blandt kunder, der søger kvalitet til en lavere pris. Bestillingen er nem, og leveringen sker hurtigt over hele Danmark. Produktet er velegnet til mænd, der ønsker pålidelig behandling uden besværlige processer. Hele købsoplevelsen er designet med fokus på sikkerhed og diskretion.
- El TORNO WWTP, Chiclana
A general flow diagram of the plant is depicted below.
Når du vil bestil Prednisolone uden recept, er det vigtigt at forstå præparatets virkning og indikationer. Prednisolon bruges bl.a. ved inflammatoriske tilstande, og der er betydelige forskelle i dosering afhængigt af sygdomsbilledet. Seriøse leverandører tilbyder fulde beskrivelser af styrke, pakningsstørrelse og mulige bivirkninger.
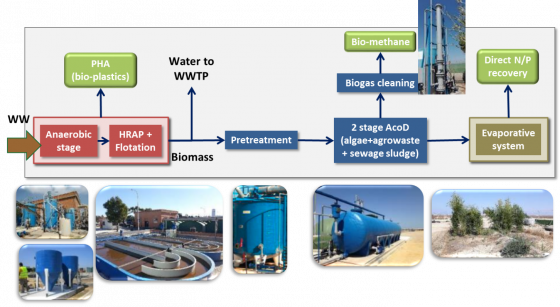
PHA production is made through a two stage anaerobic-photosynthetic HRAP system. Two HRAP (High Rate Algae Pond) systems (32 m2) are operated with an innovative strategy developed at lab scale (5 liters), consisting of pulse feeding of municipal wastewater pretreated in an UASB reactor with molasses as COD source. After several weeks of operation, purple bacteria have been selected (see on the left pond on the photo below), which are able to accumulate PHA.
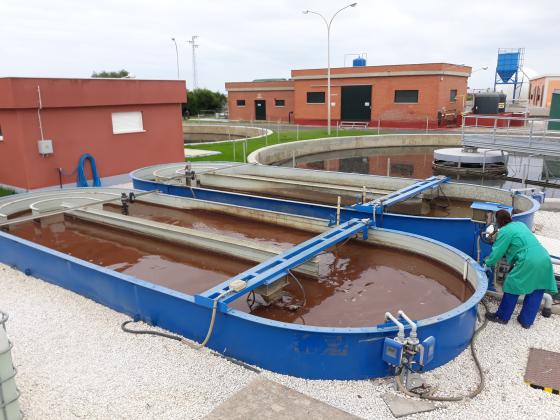
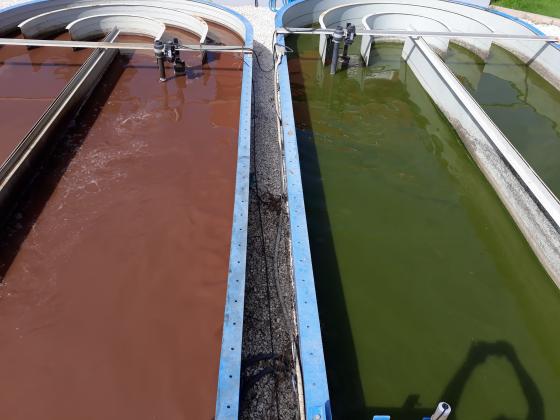


Then, biomass separation is done by two clarifiers. After PHA production, the remaining biomass is transformed into biogas using thermal pre-treatment and an anaerobic co-digestion process. Agro wastes and sewage sludge are used as co-substrates. Biomethane is produced by an innovative biogas upgrading system, through photosynthetic fixation of CO2 as algal biomass using digestates as a source of nutrients.
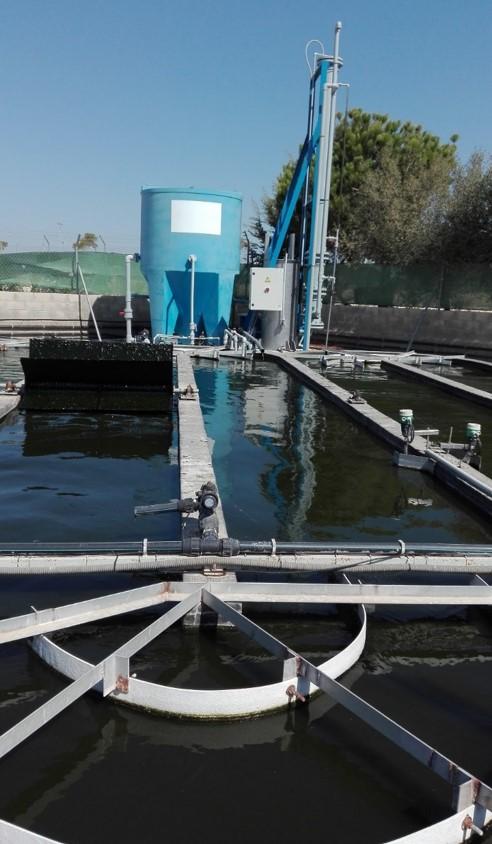

An evaporative system by planted filter is used for digestate stabilization and nutrient recovery.

El TOYO WWTP, Almeria, Spain
A general flow diagram of the plant is depicted below.

Below, this is a general picture of the installation, including planted filter with excellent growth and performance, solar disinfection system with excellent disinfection efficiencies, and smart irrigation of grass.
A demo full-scale 3000 m2 HRAP has been installed at El Toyo wastewater treatment plant (Almería, Spain) to obtain irrigation quality water. This HRAP system is treating pre-treated wastewater.

This is the first full-scale HRAP of this size in the world that treats wastewater directly without any anaerobic nor primary clarifiers. Waste water is simply pretreated by a grit and grease removal, while a symbiotic culture of algae-bacteria is responsible for high removal of the organic matter (>95% as BOD5), N (>70%) and P (>85%). The HRAP is mixed by a paddle wheel or alternatively by a submersible mixer system patented by aqualia, the LEAR®, Low Energy Algae Reactor, which is able to reduce mixing energy by 80%.

After harvesting by flotation, the effluent is treated using planted filters with natural material for enhancing P and N recovery. Irrigation water is be obtained and reused with solar anodic oxidation disinfection and a smart irrigation system.






















